HEALTHCARE COST AND UTLIZATION PROJECT – HCUP
A FEDERAL-STATE-INDUSTRY PARTNERSHIP IN HEALTH DATA
Sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
INTRODUCTION TO
THE HCUP NATIONWIDE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT SAMPLE (NEDS)
2016
| Please read all documentation carefully.
THE 2016 NEDS CONTAINS ICD-10-CM/PCS CODES The 2016 NEDS includes a full calendar year of data with diagnosis and procedure codes reported using the ICD-10-CM/PCS coding system. The 2016 NEDS file structure is different than 2015 which included both ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM/PCS coding. The 2016 file structure is similar to 2014 and earlier years, although data elements derived from AHRQ software tools are not included because the ICD-10-CM/PCS versions are still under development. |
| These pages provide an introduction to the 2016 NEDS.
For full documentation and notification of changes, visit the HCUP User Support (HCUP-US) website at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov. |
Issued September 2018
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP)
Phone: (866) 290-HCUP (4287)
Email: hcup@ahrq.gov
website: www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov
NEDS Data and Documentation Distributed by:
HCUP Central Distributor
Phone: (866) 556-4287 (toll-free)
Fax: (866) 792-5313
Email: HCUPDistributor@ahrq.gov
Table of Contents
Skip Table of Contents
HCUP NATIONWIDE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT SAMPLE (NEDS)
|
|
***** REMINDER ***** |
All users of the NEDS must take the online HCUP Data Use Agreement (DUA) training course, and read and sign a Data Use Agreement.a Authorized users of HCUP data agree to the following restrictions:b
Any violation of the limitations in the Data Use Agreement is punishable under Federal law by a fine of up to $10,000 and up to 5 years in prison. Violations may also be subject to penalties under State statutes. |
a The online Data Use Agreement training session and the Data Use Agreement are available on the HCUP HCUP-US website at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov. |
HCUP CONTACT INFORMATION
All HCUP data users, including data purchasers and collaborators, must complete the online HCUP Data Use Agreement (DUA) Training Tool, and read and sign the HCUP Data Use Agreement. Proof of training completion and signed Data Use Agreements must be submitted to the HCUP Central Distributor as described below.
The online DUA training course is available at: www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/dua.jsp.
The HCUP Nationwide Data Use Agreement is available on the AHRQ-sponsored website at: www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov
HCUP Central Distributor
Data purchasers will be required to provide their DUA training completion code and will execute their DUAs electronically as a part of the online ordering process. The DUAs and training certificates for collaborators and others with access to HCUP data should be submitted directly to the HCUP Central Distributor using the contact information below.
The HCUP Central Distributor can also help with questions concerning HCUP database purchases, current orders, training certificate codes, or invoices, if your questions are not covered in the Purchasing FAQs on the Online HCUP Central Distributor website.
Phone: (866)556-HCUP (4287) (toll free)
Email: HCUPDistributor@AHRQ.gov
Fax: (866)792-5313 (toll free in the United States)
HCUP User Support:
Information about the content of the HCUP databases and Requirements for Publishing with HCUP Data is available on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov). For questions about using the HCUP databases, software tools, supplemental files, and other HCUP products, or about data use retrictions and publishing with the data, please review the HCUP Frequently Asked Questions or contact HCUP User Support:
HCUP FAQs:
www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/faq.jsp
Phone: (866)290-HCUP (4287) (toll free)
Email: hcup@ahrq.gov
|
WHAT IS THE NATIONWIDE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT SAMPLE (NEDS)?
|
|
|
WHAT'S NEW IN THE 2016 NEDS?
|
|
|
UNDERSTANDING THE NEDS
|
|
HEALTHCARE COST AND UTILIZATION PROJECT — HCUP
A FEDERAL-STATE-INDUSTRY PARTNERSHIP IN HEALTH DATA
Sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
HCUP NATIONWIDE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT SAMPLE (NEDS)
ABSTRACT
The Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) is part of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) that is sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ).
The NEDS was created to enable analyses of emergency department (ED) utilization patterns and to support research, public health professionals, administrators, policymakers, and clinicians in their decision-making regarding this critical source of care. The ED serves a dual role in the U.S. healthcare system infrastructure, as a point of entry for approximately 50 percent of inpatient hospital admissions and as a setting for treat-and-release outpatient visits.1 The NEDS has many research applications, because it contains information about geographic, hospital, and patient characteristics as well as descriptions of the nature of the visits (i.e., common reasons for ED visits, including injuries).
The NEDS is the largest all-payer ED database that is publicly available in the United States, containing information from 33 million ED visits at 953 hospitals that approximate a 20-percent stratified sample of U.S. hospital-owned EDs. Weights are provided to calculate national and encounter-level estimates representing 144 million ED visits in 2016.
The NEDS is made possible by the voluntary participation of statewide data organizations that provide HCUP with data from ED visits that may or may not have resulted in hospital admission. Thirty-seven HCUP Partner organizations participated in the 2016 NEDS. See Appendix A, Table A.1 for a list of HCUP Partner organizations participating in the NEDS.
By stratifying on important hospital characteristics, the NEDS is designed to be representative of U.S. hospital-owned EDs. Stratified sampling is based on the following five hospital characteristics:
Because ICD-10-CM/PCS was introduced October 1, 2015, trends that rely on diagnosis and procedures may be interrupted. Analyses that do not rely on diagnosis and procedure coding should not be affected.
Access to the NEDS is open to users who sign Data Use Agreements. Uses are limited to research and aggregate statistical reporting.
For more information on the NEDS, visit the AHRQ-sponsored HCUP-US website at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/nedsdbdocumentation.jsp.
INTRODUCTION TO THE NATIONWIDE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT SAMPLE (NEDS)
Overview of NEDS Data
The Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) was created to enable analyses of emergency department (ED) utilization patterns and to support research, public health professionals, administrators, policymakers, and clinicians in their decision-making regarding this critical source of care. The ED serves a dual role in the U.S. healthcare system infrastructure, as a point of entry for approximately 50 percent of inpatient hospital admissions and as a setting for treat-and-release outpatient visits.2 The NEDS has many research applications, because it contains information about geographic, hospital, and patient characteristics as well as the nature of visits (e.g., common reasons for ED visits, acute and chronic conditions, and injuries).
NEDS Data Sources, Hospitals, and ED Visits
The number of States, hospital-owned EDs, and ED visits included in the NEDS varies by year (Table 1). The specific HCUP Partner organizations that contribute to the NEDS are identified in Appendix A, Table A.1.
Table 1. Number of States, Hospital-Owned Emergency Departments, and Records in the NEDS by Year
| Data Year | HCUP States in the NEDS | Number of Hospital-Owned EDs | Number of ED Visits, Unweighted | Number of ED Visits, Weighted for National Estimates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | AR, AZ, CA, CT, DC, FL, GA, HI, IA, IL, IN, KS, KY, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, MS, MT, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, OR, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WI, and WY (Added OR and MS) | 953 | 32,680,232 | 144,842,742 |
| 2015 | AR, AZ, CA, CT, DC, FL, GA, HI, IA, IL, IN, KS, KY, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, MT, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WI, and WY (Added TX) | 953 | 31,465,407 | 143,469,670 |
| 2014 | AR, AZ, CA, CT, DC, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, MT, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, WI, and WY (Added DC, MT, and WY) | 945 | 31,026,417 | 137,807,901 |
| 2013 | AR, AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, MN, MO, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added AR; ME data were not available) | 947 | 29,581,718 | 134,869,015 |
| 2012 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI | 950 | 31,091,029 | 134,399,179 |
| 2011 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added ND; NH data were not available) | 951 | 29,421,411 | 131,048,605 |
| 2010 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, MN, MO, NC, NE, NJ, NV, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added NV; ME and NH data were not available) | 961 | 28,584,301 | 128,970,364 |
| 2009 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, IL, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NC, NE, NH, NJ, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added IL) | 964 | 28,861,047 | 128,885,040 |
| 2008 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, KY, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NC, NE, NH, NJ, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added KY) | 980 | 28,447,148 | 124,945,264 |
| 2007 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NC, NE, NH, NJ, NY, OH, RI, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI (Added NC, NY, RI) | 966 | 26,627,923 | 122,331,739 |
| 2006 | AZ, CA, CT, FL, GA, HI, IA, IN, KS, MA, MD, ME, MN, MO, NE, NH, NJ, OH, SC, SD, TN, UT, VT, and WI | 955 | 25,702,597 | 120,033,570 |
Appendix A, Figure A.1 represents the geographic distribution of the 37 HCUP Partner organizations participating in the 2016 NEDS. Based on U.S. Census Bureau data, the HCUP NEDS States with the District of Columbia account for 68.7 percent of the U.S. population in 2016. The 37 Partner organizations account for 78.2 percent of the ED visits reported in the 2016 American Hospital Association (AHA) Annual Survey Database. Details on the percentage of population and ED visits by region are provided in Appendix A, Table A.2.
Identification of HCUP Records with Emergency Department Services
Records for ED events are contained in two existing HCUP databases:
Both of these HCUP databases contain a core set of clinical and non-clinical data elements that are defined in a uniform scheme for all patients, regardless of payer. This scheme makes it possible to combine records across databases.
Selection of ED records from the SEDD and SID for use in the NEDS was based on evidence of ED services reported on the record. Differing methods are used by HCUP Partner organizations for identifying ED records. The HCUP criteria for identifying an ED record (i.e., a discharge record for a patient with an ED even) look for at least one of the following conditions to be true:
Two of the 37 Partner organizations (CA and MA) provided a source file that contained only ED treat-and-release records. Because the data source provided a dedicated outpatient ED file, all of the SEDD records were considered to be ED records, even though information was not available to determine if HCUP criteria were met.
Partner-Specific Restrictions
Some HCUP Partner organizations that contributed data to the NEDS imposed restrictions on the release of certain data elements or on the number and types of hospitals that could be included in the database. In addition, because of confidentiality laws, some data sources were prohibited from providing HCUP with discharge records that indicated specific medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS or behavioral health. Detailed information on these Partner-specific restrictions is available in Appendix B.
ICD-10-CM/PCS Started October 1, 2015 at the Beginning of Fiscal Year 2016
On October 1, 2015, the United States transitioned from using ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM/PCS code sets for reporting medical diagnoses and inpatient procedures.3 ICD-10-CM/PCS consists of two parts:
The HCUP-US website has a section on ICD-10-CM/PCS Resources that summarizes key issues for researchers using HCUP and other administrative databases that include ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM/PCS coding. The Web page provides general guidance and forewarning to users analyzing outcomes that may be affected by the transition to the ICD-10-CM/PCS coding system and lists other related Web resources.
File Structure of the NEDS
Because of the size of the NEDS and the difference in information collected on records for patients admitted into the hospital directly from the ED (SID records) and for ED patients that are not admitted (SEDD records), the NEDS is divided into four types of files:
File Structure of the 2016 NEDS
The 2016 NEDS is an annual, calendar year file that includes data with diagnosis and procedure codes reported using the ICD-10-CM/PCS coding system. The file structure of the 2016 NEDS is similar to the file structure of the NEDS prior to 2015 with one exception, data elements derived from AHRQ software tools are not available in the 2016 NEDS because the ICD-10-CM/PCS versions are still under development. For users interested in applying the AHRQ software tools to the ICD-10-CM/PCS data in the 2016 NEDS, beta versions of the AHRQ software tools are available for download on the HCUP Tools & Software section of the HCUP-US website. A tutorial is available to users interested in applying the AHRQ software tools to the 2016 NEDS at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/tutorials.jsp.
File Structure of the 2015 NEDS
The NEDS data files are annual, calendar-year files based on discharge date for all years except 2015. The introduction of ICD-10-CM/PCS in the United States on October 1, 2015 means that the 2015 NEDS includes a combination of codes:
To alert users to this change in the ICD coding scheme, the file structure of the 2015 NEDS differs from the annual files for other data years in three primary ways:
More information about the file structure of the 2015 NEDS is available in the Introduction to the NEDS, 2015, and on HCUP-US website at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/nedsdbdocumentation.jsp.
NEDS Data Elements
The coding of data elements in the NEDS is consistent with other HCUP databases. The following three objectives guided the definition of data elements in all HCUP databases:
More information on the coding of HCUP data elements is available on HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/coding.jsp).
After analyzing the availability of information from the HCUP Partner organizations, a set of common fields to be available in the NEDS was created. The NEDS contains more than 100 clinical and non-clinical variables provided in a hospital discharge abstract, such as:
Appendix C identifies the data elements in each NEDS file:
The tables in Appendix C provide summary documentation for the data. Please refer to the NEDS documentation located on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/nedsdde.jsp) for comprehensive information about data elements.
Getting Started
The HCUP NEDS is distributed as comma-separated value (CSV) files delivered via secure digital download from the Online HCUP Central Distributor. The files are compressed and encrypted with SecureZIP® from PKWARE.
The NEDS product is downloaded in a single zipped file for each year which contains several data-related files and accompanying documentation. The four data-related files include the following compressed files:
The total size of the CSV version of the NEDS is 9 GB. The NEDS files loaded into SAS are about 7 GB. In SAS, the largest use of space typically occurs during PROC SORT, which requires work space about three times the size of the file. Thus, the NEDS files would require at least 22 GB of available workspace to perform a sort procedure. Most SAS data steps will require twice the storage of the file, so that both the input and output files can coexist. The NEDS files loaded into SPSS are about 19 GB. Because Stata loads the entire file into memory, it may not be possible to load every data element in the NEDS Core file into Stata. Stata users will need to maximize memory and use the "_skip" option to select a subset of data elements. More details are provided in the Stata load programs.
With a file of this size and without careful planning, space could easily become a problem in a multi-step program. It is not unusual to have several versions of a file marking different steps while preparing it for analysis, and there may be more versions for the actual analyses. Therefore, the amount of space required could escalate rapidly.
Decompressing the NEDS Files
To extract the data files from the compressed download file, follow these steps:
Downloading and Running the Load Programs
Programs to load the data into SAS, SPSS, or Stata, are available on the HCUP-US website. To download and run the load programs, follow these steps:
NEDS Documentation
Comprehensive documentation for the NEDS files is available on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/nedsdbdocumentation.jsp). Users of the NEDS can access complete file documentation, including variable notes, file layouts, summary statistics, and related technical reports. Similarly, data users can download SAS, SPSS, and Stata load programs. These important resources help the user understand the structure and content of the NEDS and aid in using the database. Appendix A, Table A.3 details the comprehensive NEDS documentation available on HCUP-US.
HCUP Online Tutorials
For additional assistance, AHRQ has created the HCUP Online Tutorial Series, a series of free, interactive courses that provide information on using HCUP data and tools and training on technical methods for conducting research with HCUP data. Topics include an HCUP Overview Course and these tutorials:
New tutorials are added periodically. The Online Tutorial Series is located on the HCUP-US website at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/tutorials.jsp.
SAMPLING DESIGN OF THE NEDS
The NEDS is built using a 20 percent stratified sample of hospital-owned EDs in the United States. The main objective of a stratified sample is to ensure that it is representative of the target universe. By stratifying on important hospital characteristics, the NEDS represents a "microcosm" of EDs in the U.S. For example, by including trauma center designation in the sampling strategy, the NEDS has the same percentage of trauma hospitals as the entire U.S. The NEDS contains all of the ED visits for the sample of hospital-owned EDs selected.
Universe of Hospital-Owned Emergency Departments
A feasibility study performed in 2008 assessed several possible data sources for the universe of hospital-owned EDs in the United States: the American Hospital Association (AHA) Annual Survey Database (Health Forum, LLC © 2007); Verispan, LLC databases (now called IMS Health, Inc.); and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) Hospital Cost Reports. The AHA Annual Survey Database has the best data to apply for a couple of reasons. First, the AHA data provide the necessary hospital characteristics, such as ownership type and teaching status, and also report total ED visits for hospitals. Second, the crosswalk linkage from the HCUP databases to the AHA data is already established. The universe of hospital-owned EDs is therefore defined as the AHA community, nonrehabilitation hospitals that reported total ED visits. The AHA defines community hospitals as "all non-Federal, short-term, general, and other specialty hospitals."4 Included among community hospitals are pediatric institutions, public hospitals, and academic medical centers.
Sampling Frame of the NEDS
The sampling frame of the NEDS is limited to a subset of the universe: hospital-owned EDs in the States and District of Columbia for which HCUP ED data (SID and SEDD) are available. The list of hospital-owned EDs in the frame consists of all AHA community, nonrehabilitation hospitals that report total ED visits in each of the frame States and District of Columbia that could be matched to the ED data provided to HCUP. If an ED in the AHA survey could not be matched to the ED data provided by the HCUP data source, it was eliminated from the sampling frame (but not from the target universe).
Stratification Variables
The following hospital characteristics were used for sample stratification: U.S. Census region, trauma center designation, urban-rural location of the hospital, ownership, and teaching status. ED bed size was not used because no data source for this information could be identified. A number of data sources report the bed size of the hospital, but no source distinguishes between inpatient and ED beds.
The NEDS stratification variables are described below and detailed in Appendix A, Table A.4.
U.S. Census Region
The four Census regions – Northeast, Midwest, South, and West – were used to stratify EDs by geographic location because practice patterns may vary substantially by region. Appendix A, Figure A.1 shows the NEDS States by region.
Trauma Centers
A trauma center is a hospital that is equipped to provide comprehensive emergency medical services 24 hours a day, 365 days per year to patients with traumatic injuries. In 1976, the American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma (ACS/COT) defined five levels of trauma centers:5
The ACS/COT has a program that verifies hospitals as trauma level I, II, or III.6 It is important to note that although all level I, II, and III trauma centers offer a high level of trauma care, there may be differences in the specific services and resources offered by hospitals of different levels. Trauma levels IV and V are designated at the State level (and not by ACS/COT) with varying criteria applied across States.
The level of the trauma centers in the NEDS was identified using the Trauma Information Exchange Program (TIEP) database, a national inventory of trauma centers in the U.S collected by the American Trauma Society.7 The TIEP database identifies all U.S. trauma centers that are level I, II, and III that treat both adults and children. TIEP includes some information on trauma centers within children's hospitals, but this is not their focus. To ensure that all of trauma centers are identified for the NEDS, the ACS/COT list of trauma centers and all State-specific websites on emergency services are reviewed to identify any additional trauma centers within children's hospitals and their associated trauma levels.
The stratum for trauma center in the NEDS was limited to trauma levels I, II, and III. Level IV and V centers were not included because the criteria for designation varied across States. For hospital confidentiality purposes, a collapsed stratification was necessary if the strata size in the universe or frame was less than two hospitals. The grouping of trauma centers into collapsed categories varied by data year:
The change between the 2010 and 2011 NEDS was prompted by differences between injury-related services provided by trauma level I and II centers versus injury-related services provided by trauma level III centers. Services at trauma level III centers were more similar to nontrauma hospitals.
Urban-Rural Location of the ED
The urban-rural location of hospital-owned EDs was determined based on the county in which the hospital was located. The categorization is based on Urban Influence Codes (UIC).8 In the 2014 NEDS, the categorization is a simplified adaptation of the 2013 version of the UIC. Prior to 2014, the categorization is a simplified adaptation of the 2003 version of the UIC. The twelve detailed UIC categories are combined into four broader categories:
If the strata size in the universe or frame was less than two hospitals, a collapsed stratification of metropolitan (large and small), non-metropolitan (micropolitan and non-urban residual), small metropolitan and micropolitan,9 or all areas10 was necessary.
Teaching Status
A hospital-owned ED is considered a teaching hospital if it has one or more Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) approved residency program, is a member of the Council of Teaching Hospitals (COTH) or has a ratio of full-time equivalent interns and residents to beds of .25 or higher. Beginning with the 2014 NEDS, there is an increase in the number of hospitals identified as teaching facilities because the AHA Annual Survey showed an increase in facilities with approved residency programs. About this time, the ACGME became the primary organization for residency training approval. Because there are very few teaching hospitals in micropolitan and rural areas, teaching status was only used to stratify EDs in metropolitan areas.
Hospital Ownership
Hospital ownership or control was categorized according to information reported in the AHA Annual Survey Database. Ownership categories include:
When there were enough hospitals of each type, EDs were stratified into public, voluntary, and proprietary categories. If necessary, because of small strata size in the universe, a collapsed stratification of public versus private was used; the voluntary, non-profit and proprietary/for-profit hospitals were combined to form a single "private" category. Stratification based on ownership or control was not advisable in some regions because of the dominance of one type of hospital (e.g., Northeast).
Sample Weights
To obtain nationwide estimates, weights were developed using the AHA universe as the standard. These were developed separately for analyses of hospital-owned EDs and ED visits. Hospital-level weights were developed to extrapolate NEDS sample EDs to the universe of hospital-owned EDs. Similarly, discharge-level discharge weights were developed to extrapolate NEDS sample ED visits to the universe of ED visits.
Hospital Weights
Hospital weights to the universe were calculated after sampling and by strata. Hospital-owned EDs were stratified on the same variables that were used for sampling: geographic region, trauma center designation, urban-rural location, teaching status, and ownership or control. The strata that were collapsed for sampling were also collapsed for sample weight calculations. Within each stratum, s, each ED in the NEDS sample received a weight:
Discharge Weights
Discharge weights to the universe were calculated after sampling and by strata. Hospital-owned EDs were stratified in a manner similar to that for universe hospital-weight calculations. Within stratum, s, for hospital, i, the universe weight for each visit in the NEDS sample, was calculated as:
Final NEDS Sample
The target universe for the NEDS was: (1) community, nonrehabilitation hospital-owned EDs in the United States that were included in the 2016 AHA Annual Survey Database, and (2) reported total ED visits. Excluded were a handful of non-rural hospitals that reported less than ten ED visits in a year.
The NEDS sampling frame included hospital-owned ED events from community, nonrehabilitation hospitals in the 37 HCUP Partner organizations that provided discharge abstracts on patients admitted to the hospital through the ED and on patients treated and released or transferred to another hospital from the ED. The HCUP hospitals were required to be represented in the AHA data and have no more than 90 percent of their ED visits resulting in admission. Appendix A, Table A.5 lists the final target universe and sampling frame for the NEDS.
The NEDS is a stratified probability sample of hospital-owned EDs in the frame. Sampling probabilities were calculated to select 20 percent of the universe contained in each stratum, which was defined by region, trauma designation, urban-rural location, teaching status, and hospital ownership or control. A sample size of 20 percent was based on previous experience with similar research databases. A larger sample would be cumbersome for data users, given that a 20 percent sample contains about 30 million records. A 20 percent sample also enables the user to split the NEDS into two 10 percent subsamples for estimation and validation of models.
Using the universe of U.S. hospital-owned EDs, strata were defined by region, trauma designation, urban-rural location, teaching status, and hospital ownership or control. Strata with less than two hospitals in the universe and frame were collapsed with adjacent stratum based on urban-rural location, trauma designation, or ownership or control. Prior to sampling, the list of frame hospitals within each stratum is sorted as follows to ensure geographic representation within strata: (1) sorted by the first three digits of the hospital's ZIP Code and (2) sorted by a random number within the three-digit ZIP Code.11 After stratifying and sorting the frame hospitals, a random sample of up to 20 percent of the total number of hospital-owned EDs in the U.S. was selected within each stratum. A stratum with a shortfall was defined as having an insufficient number of EDs in the frame to meet the threshold of 20 percent of the universe for that stratum. In strata with shortfalls, the sampling rate from the universe was less than 20 percent and all possible EDs in the frame were selected for the NEDS. In contrast, the sampling rate is larger than 20 percent in some strata because protecting hospital confidentiality required a minimum of two sampled EDs in each stratum. Appendix A, Table A.6 lists the sampling rates by stratum for the NEDS.
HOW TO USE THE NEDS FOR DATA ANALYSIS
This section provides a brief synopsis of special considerations for using the NEDS. For more details, refer to the comprehensive documentation on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/).
All persons using the NEDS (whether or not they are the original recipient of the data) must complete the on-line Data Use Agreement Training Course available on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/dua.jsp) and then read and sign a Data Use Agreement. A copy of the signed Data Use Agreements must be sent to the HCUP Central Distributor.
Limitations of the NEDS
The NEDS contains about 30 million ED records and over 100 clinical and non-clinical data elements. A multitude of research studies can be conducted with the data, but there are some limitations.
Identifying Different Types of ED Events
The HCUP data element ED event distinguishes among the different types of ED events: Appendix A, Table A.7 provides the number and percentage of records in the 2016 NEDS for each of the five types of ED event types.
Calculating National Estimates
To produce national estimates, weights MUST be used.
Because the NEDS is a stratified sample, proper statistical techniques must be used to calculate standard errors and confidence intervals. For detailed instructions, refer to the HCUP Methods Series report #2003-02 Calculating Nationwide Inpatient Sample Variances on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov). The HCUP Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) prior to 2012 used stratified sample design similar to the NEDS, so techniques appropriate for the NIS prior to 2012 are also appropriate for the NEDS.
When creating national estimates, it is a good idea to check results against other data sources, if available. Summary benchmarks for national estimates from the NEDS are provided in Appendix D. Also included in Appendix D are comparable estimates from other ED data sources. For example, the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) has an ED component and publishes national health statistics annually.
To ensure that weights are used appropriately and estimates and variances are calculated accurately, researchers can also use HCUPnet, the free online query system (https://datatools.ahrq.gov/hcupnet). HCUPnet is a Web-based query tool for identifying, tracking, analyzing, and comparing statistics on hospitals at the national, regional, and State levels. HCUPnet is a Web-based query tool for identifying, tracking, analyzing, and comparing statistics on hospitals at the national, regional, and State levels. HCUPnet offers easy access to national statistics and trends as well as selected State statistics about hospital stays, ED visits and ambulatory surgeries. This tool provides step-by-step guidance, helping researchers to quickly obtain the statistics they need. HCUPnet generates statistics using the HCUP databases.
Choosing Data Elements for Analysis
For all data elements to be used in the analysis, the user should first perform descriptive statistics and examine the range of values, including number of missing cases. Summary statistics are available on the HCUP-US website under Database Documentation for the NEDS (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/nedssummstats.jsp). When anomalies (such as large numbers of missing cases) are detected, descriptive statistics can be performed by region for that variable to determine whether or not there are region-specific differences. Sometimes, performing descriptive statistics by hospital (HOSP_ED) can be helpful in detecting hospital-specific data anomalies.
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM/PCS Diagnosis and Procedure Codes and CPT Procedure Codes
Missing Values
Missing data values can compromise the quality of estimates. For example, if the outcome for ED visits with missing values is different from the outcome for ED visits with valid values, then sample estimates for that outcome will be biased and inaccurately represent the ED utilization patterns. There are several techniques available to help overcome this bias. One strategy is to use imputation to replace missing values with acceptable values. Another strategy is to use sample weight adjustments to compensate for missing values. Descriptions of such data preparation and adjustment are outside the scope of this report; however, it is recommended that researchers evaluate and adjust for missing data, if necessary.
Alternatively, if the cases with and without missing values are assumed to be similar with respect to their outcomes, no adjustment may be necessary for estimates of means and rates because the non-missing cases would be representative of the missing cases. However, some adjustment may still be necessary for the estimates of totals. Sums of data elements (such as aggregate ED charges) containing missing values would be incomplete because cases with missing values would be omitted from the calculations. Estimates of the sum of charges should use the product of the number of cases times the average charge to account for records with missing information.
Variance Calculations
It may be important for researchers to calculate a measure of precision for some estimates based on the NEDS sample data. Variance estimates must take into account both the sampling design and the form of the statistic. The sampling design consisted of a stratified, single-stage cluster sample. A stratified random sample of hospital-owned EDs (clusters) was drawn and then all ED visits were included from each selected hospital. To accurately calculate variances from the NEDS, appropriate statistical software and techniques must be used. For detailed instructions, refer to the HCUP Methods Series report #2003-02 Calculating Nationwide Inpatient Sample Variances on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/). The HCUP Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) prior to 2012 used stratified sample design similar to the NEDS, so techniques appropriate for the NIS prior to 2012 are also appropriate for the NEDS.
A multitude of statistics can be estimated from the NEDS data. Several computer programs that calculate statistics and their variances from sample survey data are listed in the next section. Some of these programs use general methods of variance calculations (e.g., the jackknife and balanced half-sample replications) that take into account the sampling design. However, it may be desirable to calculate variances using formulas specifically developed for certain statistics.
These variance calculations are based on finite-sample theory, which is an appropriate method for obtaining cross-sectional, nationwide estimates of outcomes. According to finite-sample theory, the intent of the estimation process is to obtain estimates that are precise representations of the nationwide population at a specific point in time. In the context of the NEDS, any estimates that attempt to accurately describe characteristics and interrelationships among hospitals and ED visits during a specific year should be governed by finite-sample theory. Examples would be estimates of expenditure and utilization patterns.
Alternatively, in the study of hypothetical population outcomes not limited to a specific point in time, the concept of a "superpopulation" may be useful. Analysts may be less interested in specific characteristics of the finite population (and time period) from which the sample was drawn than they are in hypothetical characteristics of a conceptual superpopulation from which any particular finite population in a given year might have been drawn. According to this superpopulation model, the nationwide population in a given year is only a snapshot in time of the possible interrelationships among hospital, market, and discharge characteristics. In a given year, all possible interactions between such characteristics may not have been observed, but analysts may wish to predict or simulate interrelationships that may occur in the future.
Under the finite-population model, the variances of estimates approach zero as the sampling fraction approaches one. This is the case because the population is defined at that point in time and because the estimate is for a characteristic as it existed when sampled. This is in contrast to the superpopulation model, which adopts a stochastic viewpoint rather than a deterministic viewpoint. That is, the nationwide population in a particular year is viewed as a random sample of some underlying superpopulation over time. Different methods are used for calculating variances under the two sample theories. The choice of an appropriate method for calculating variances for nationwide estimates depends on the type of measure and the intent of the estimation process.
Computer Software for Weighted and Variance Calculations
The hospital weights are useful for producing hospital-level statistics for analyses that use the hospital-owned ED as the unit of analysis. In contrast, the discharge weights are useful for producing visit-level statistics for analyses that use the ED visit as the unit of analysis.
In most cases, computer programs are readily available to perform these calculations. Several statistical programming packages allow weighted analyses.13 For example, nearly all SAS procedures incorporate weights. In addition, several statistical analysis programs have been developed to specifically calculate statistics and their standard errors from survey data. Version 8 or later of SAS contains procedures (PROC SURVEYMEANS and PROC SURVEYREG) for calculating statistics based on specific sampling designs. Stata and SUDAAN are two other common statistical software packages that perform calculations for numerous statistics arising from the stratified, single-stage cluster sampling design. Examples of the use of SAS, SUDAAN, and Stata to calculate NIS variances are presented in the special report Calculating Nationwide Inpatient Sample Variances on the HCUP-US website (www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov). Although the examples using the NIS also apply to the NEDS, it should be noted that the NEDS is a much larger data set. Please consult the documentation for the different software packages concerning the use of large databases. For an excellent review of programs to calculate statistics from survey data, visit the following website: www.hcp.med.harvard.edu/statistics/survey-soft/. ![]()
The NEDS includes a Hospital Weights File with variables required by these programs to calculate finite-population statistics. The file includes synthetic hospital identifiers (Primary Sampling Units or PSUs), stratification variables, and stratum-specific totals for the numbers of ED visits and hospitals so that finite-population corrections can be applied to variance estimates.
In addition to these subroutines, standard errors can be estimated by validation and cross-validation techniques. Given that a very large number of observations will be available for most NEDS analyses, it may be feasible to set aside a part of the data for validation purposes. Standard errors and confidence intervals then can be calculated from the validation data.
If the analytic file is too small to set aside a large validation sample, cross-validation techniques may be used. For example, ten-fold cross-validation would split the data into 10 subsets of equal size. The estimation would take place in 10 iterations. In each iteration, the outcome of interest is predicted for one-tenth of the observations by an estimate based on a model that is fit to the other nine-tenths of the observations. Unbiased estimates of error variance are then obtained by comparing the actual values to the predicted values obtained in this manner.
COMPARABLE ED DATA SOURCES
To aid in understanding of NEDS, national estimates from the NEDS are compared to available sources of similar data (Table 2). Each of the following ED data sources has potential for use in research addressing ED utilization and policy.
Table 2. Sources of Emergency Department (ED) Data by Type
| Type of ED Data | ED Data Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| National inventories of EDs | American Hospital Association (AHA) Annual Survey Database | Database containing characteristics and descriptions of hospitals in the U.S. reported by hospitals via survey. Owned by Health Forum. |
| National Emergency Department Inventory (NEDI) — USA | Inventory of ED locations in the U.S. and annual ED visit volume that integrates information from the AHA Annual Survey Database, the Hospital Market Profiling Solution,© Internet searches, and direct communication with hospital staff. Created by the Emergency Medicine Network (EMNet). The NEDI is only available every other year and was not created for 2016. | |
| ED visit information from a sample of EDs | HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) | Nationwide sample drawn from the HCUP SID and SEDD, stratified and weighted to be nationally representative of ED visits and facilities. Sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). |
| National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) | National probability sample survey of utilization and provision of ambulatory services in hospital emergency and outpatient departments. Sponsored by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of the DHHS' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). | |
| National Electronic Injury Surveillance System - All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP) | National probability sample providing counts of injuries seen in the ED. Sponsored by the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control (NCIPC) of the DHHS' CDC and the US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC). | |
| ED visit information from a sample of patients | National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) | A comprehensive survey of the civilian non-institutionalized population residing in the United States at the time of the interview. Sponsored by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of the DHHS CDC. |
Information on total ED visits in 2016 for the U.S. was available from three data sources (AHA, NEDS, and NHIS)14. Appendix D, Figure D.1, displays the range of total ED visits; Appendix D, Table D.1 lists the total ED visits in the U.S and the totals by census region. The total U.S. ED visit counts are relatively consistent across the data sources. The South consistently had the highest number of ED visits.
Information on the total number of ED visits by region and the percentage of all ED visits resulting in inpatient admissions are available from one data source (NEDS) and are displayed in Appendix D, Table D.2.
Estimates of the number of hospital-owned EDs by ED visit volume are available from two data sources (NEDS and AHA) and are displayed in Appendix D, Table D.3.
Estimates of the number of ED visits related to nonfatal ED visits are available from two data sources (NEDS and NEISS-AIP) and are displayed in Appendix D, Table D.4.
Appendix A: NEDS Introductory Information
Table A.1. HCUP Partners Participating in the 2016 NEDS
| State | HCUP Data Organization |
|---|---|
| AR | Arkansas Department of Health |
| AZ | Arizona Department of Health Services |
| CA | Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development |
| CT | Connecticut Hospital Association |
| DC | District of Columbia Hospital Association |
| FL | Florida Agency for Health Care Administration |
| GA | Georgia Hospital Association |
| HI | Hawaii Health Information Corporation |
| IA | Iowa Hospital Association |
| IL | Illinois Department of Public Health |
| IN | Indiana Hospital Association |
| KS | Kansas Hospital Association |
| KY | Kentucky Cabinet for Health and Family Services |
| MA | Massachusetts Center for Health Information and Analysis |
| MD | Maryland Health Services Cost Review Commission |
| ME | Maine Health Data Organization |
| MN | Minnesota Hospital Association |
| MO | Missouri Hospital Industry Data Institute |
| MS | Mississippi State Department of Health |
| MT | Montana Hospital Association |
| NC | North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services |
| ND | North Dakota (data provided by the Minnesota Hospital Association) |
| NE | Nebraska Hospital Association |
| NJ | New Jersey Department of Health |
| NV | Nevada Department of Health and Human Services |
| NY | New York State Department of Health |
| OH | Ohio Hospital Association |
| OR | Oregon Association of Hospitals and Health Systems Oregon Office of Health Analytics |
| RI | Rhode Island Department of Health |
| SC | South Carolina Revenue and Fiscal Affairs Office |
| SD | South Dakota Association of Healthcare Organizations |
| TN | Tennessee Hospital Association |
| UT | Utah Department of Health |
| VT | Vermont Association of Hospitals and Health Systems |
| WI | Wisconsin Department of Health Services |
| WY | Wyoming Hospital Association |
Figure A.1. HCUP States and the District of Columbia Included in the 2016 NEDS
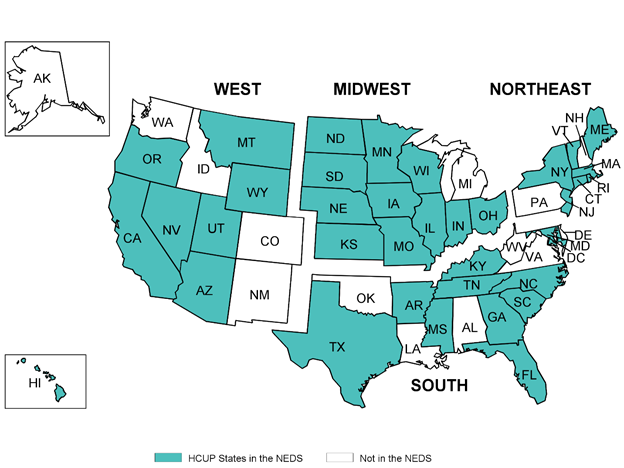
The above graphic outlines states in the NEDS by Region. In the Western region, AZ, CA, HI, MT, NV, OR, UT, WY are in the HCUP NEDS. The following states are not in the NEDS in this region - AK, CO, ID, NM, WA. In the Midwestern region, IA, IN, IL, KS, MN, MO, ND, NE, OH, SD, WI are in the HCUP NEDS. The following state is not in the NEDS in this region - MI. In the Northeastern region, CT, MA, ME, NJ, NY, RI, VT are in the HCUP NEDS. The following states are not in the NEDS in this region - NH, PA. In the Southern region, AR, DC, FL, GA, KY, MD, MS, NC, SC, TN, TX are in the HCUP NEDS. The following states are not in the NEDS in this region - AL, DE, LA, OK, VA, WV.
Table A.2. Percentage of U.S Population and ED Visits Accounted for by the 37 HCUP Organizations Participating in the NEDS, 2016
| Region | U.S. Population, 2016 | Percentage of U.S. Population in NEDS States (%) | ED Visits in the U.S., 2016 | Percentage of U.S. ED Visits in NEDS States (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 42,090,488 | 74.9 | 26,474,638 | 73.1 |
| Midwest | 58,013,129 | 85.4 | 32,939,409 | 84.3 |
| South | 97,656,072 | 79.8 | 58,096,752 | 78.6 |
| West | 59,322,406 | 77.4 | 27,331,943 | 75.0 |
| Nation | 323,127,513 | 68.7 | 144,842,742 | 78.2 |
Source: Population count from the U.S. Census Bureau, Annual Estimates of the Population for the United States, 2016, Table NST-EST2016-01. ED visits in the U.S. from the American Hospital Association Annual Survey of Hospitals, 2016.
Table A.3. NEDS-Related Reports and Database Documentation Available on the HCUP-US website
Description of the NEDS Database
Restrictions on the Use
File Specifications and Load Programs
Data Elements
Additional Resources for NEDS Data Elements
|
ICD-10-CM/PCS Data Included in the 2015-2016 NEDS
Known Data Issues
HCUP Tools: Labels and Formats
Obtaining HCUP Data
|
| Stratifier | Values |
|---|---|
| Region | 1: Northeast 2: Midwest 3: South 4: West |
| Trauma | 0: Not a trauma center
1: Trauma center level I 2: Trauma center level II 3: Trauma center level III Collapsed categories used for strata with small sample sizes 4: Nontrauma or trauma center level III (beginning in the 2011 NEDS) 8: Trauma center level I or II (in all years of the NEDS) 9: Trauma center level I, II or III (only in the 2006-2010 NEDS) |
| Urban-Rural | 1: Large metropolitan
2: Small metropolitan 3: Micropolitan 4: Non-urban residual Collapsed categories used for strata with small sample sizes 6: Any urban-rural location (used in the South in 2014) 7: Small metropolitan and micropolitan (used in the South in 2011-2015) 8: Metropolitan (large and small) 9: Non-metropolitan (micropolitan and non-urban location) |
| Teaching | 0: Metropolitan non-teaching
1: Metropolitan teaching 2: Non-metropolitan teaching and non-teaching |
| Control | 0: All (used for combining public, voluntary, and private)
1: Public – government, non-Federal 2: Voluntary – private, non-profit 3: Proprietary – private, investor-owned/for-profit 4: Private (used for combining private voluntary and proprietary) |
| Description | Number of Hospital-Owned EDs, 2016 | Number of ED Events, 2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Universe | EDs in community, nonrehabilitation U.S. hospitals that reported total ED visits in the AHA Annual Survey Database | 4,552 | 144,842,742 |
| Sampling Frame | EDs in the 36 States and the District of Columbia that provide information on ED visits that result and do not result in admission | 3,320 | 113,306,272 |
| 2016 NEDS | 20 percent sample of target universe drawn from the sampling frame | 953 | 32,680,232 |
Source: HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample, 2016
Table A.6. NEDS Sampling Rates by Region, 2016
NEDS stratum is defined by 5 digits:
1st digit - Region: (1) Northeast, (2) Midwest, (3) South, (4) West| NEDS Stratum | Number of Hospital-owned EDs | Sampling Rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEDS Stratum | AHA Universe | 20 % of Universe | Frame | Frame Shortfall | NEDS | NEDS to Universe | NEDS to Frame |
| Total | 4,552 | 954 | 3,320 | 1 | 953 | 20.9% | 28.7% |
| Northeast | |||||||
| 10100 | 82 | 17 | 58 | 0 | 17 | 20.7% | 29.3% |
| 10110 | 114 | 23 | 86 | 0 | 23 | 20.2% | 26.7% |
| 10200 | 67 | 14 | 42 | 0 | 14 | 20.9% | 33.3% |
| 10210 | 41 | 9 | 23 | 0 | 9 | 22.0% | 39.1% |
| 10420 | 53 | 11 | 39 | 0 | 11 | 20.8% | 28.2% |
| 11110 | 44 | 9 | 32 | 0 | 9 | 20.5% | 28.1% |
| 11210 | 13 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 23.1% | 60.0% |
| 12100 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 50.0% | 66.7% |
| 12110 | 22 | 5 | 14 | 0 | 5 | 22.7% | 35.7% |
| 12210 | 18 | 4 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 22.2% | 33.3% |
| 13110 | 8 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 25.0% | 25.0% |
| 13210 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 33.3% | 100.0% |
| 13800 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 28.6% | 66.7% |
| 14320 | 71 | 15 | 32 | 0 | 15 | 21.1% | 46.9% |
| 18320 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 50.0% | 100.0% |
| Midwest | |||||||
| 20100 | 112 | 23 | 101 | 0 | 23 | 20.5% | 22.8% |
| 20110 | 80 | 16 | 70 | 0 | 16 | 20.0% | 22.9% |
| 20200 | 135 | 27 | 104 | 0 | 27 | 20.0% | 26.0% |
| 20210 | 39 | 8 | 31 | 0 | 8 | 20.5% | 25.8% |
| 20321 | 49 | 10 | 43 | 0 | 10 | 20.4% | 23.3% |
| 20324 | 162 | 33 | 139 | 0 | 33 | 20.4% | 23.7% |
| 20421 | 182 | 37 | 168 | 0 | 37 | 20.3% | 22.0% |
| 20424 | 257 | 52 | 210 | 0 | 52 | 20.2% | 24.8% |
| 21100 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| 21110 | 41 | 9 | 37 | 0 | 9 | 22.0% | 24.3% |
| 21210 | 29 | 6 | 22 | 0 | 6 | 20.7% | 27.3% |
| 22100 | 20 | 4 | 19 | 0 | 4 | 20.0% | 21.1% |
| 22110 | 31 | 7 | 19 | 0 | 7 | 22.6% | 36.8% |
| 22200 | 21 | 5 | 19 | 0 | 5 | 23.8% | 26.3% |
| 22210 | 38 | 8 | 30 | 0 | 8 | 21.1% | 26.7% |
| 22920 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 25.0% | 50.0% |
| 23100 | 17 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 4 | 23.5% | 26.7% |
| 23110 | 22 | 5 | 16 | 0 | 5 | 22.7% | 31.3% |
| 23200 | 26 | 6 | 23 | 0 | 6 | 23.1% | 26.1% |
| 23210 | 25 | 5 | 21 | 0 | 5 | 20.0% | 23.8% |
| 23321 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 33.3% | 66.7% |
| 23324 | 40 | 8 | 37 | 0 | 8 | 20.0% | 21.6% |
| 23424 | 13 | 3 | 12 | 0 | 3 | 23.1% | 25.0% |
| South | |||||||
| 30101 | 28 | 6 | 22 | 0 | 6 | 21.4% | 27.3% |
| 30102 | 105 | 21 | 85 | 0 | 21 | 20.0% | 24.7% |
| 30103 | 139 | 28 | 115 | 0 | 28 | 20.1% | 24.3% |
| 30110 | 151 | 31 | 116 | 0 | 31 | 20.5% | 26.7% |
| 30201 | 58 | 12 | 31 | 0 | 12 | 20.7% | 38.7% |
| 30202 | 119 | 24 | 81 | 0 | 24 | 20.2% | 29.6% |
| 30203 | 96 | 20 | 60 | 0 | 20 | 20.8% | 33.3% |
| 30210 | 73 | 15 | 46 | 0 | 15 | 20.5% | 32.6% |
| 30321 | 63 | 13 | 52 | 0 | 13 | 20.6% | 25.0% |
| 30322 | 96 | 20 | 77 | 0 | 20 | 20.8% | 26.0% |
| 30323 | 53 | 11 | 34 | 0 | 11 | 20.8% | 32.4% |
| 30421 | 169 | 34 | 119 | 0 | 34 | 20.1% | 28.6% |
| 30422 | 169 | 34 | 121 | 0 | 34 | 20.1% | 28.1% |
| 30423 | 74 | 15 | 45 | 0 | 15 | 20.3% | 33.3% |
| 31110 | 47 | 10 | 37 | 0 | 10 | 21.3% | 27.0% |
| 31210 | 32 | 7 | 23 | 0 | 7 | 21.9% | 30.4% |
| 32110 | 25 | 5 | 22 | 0 | 5 | 20.0% | 22.7% |
| 32200 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 20.0% | 25.0% |
| 32210 | 44 | 9 | 32 | 0 | 9 | 20.5% | 28.1% |
| 32922 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 66.7% | 100.0% |
| 33100 | 18 | 4 | 13 | 0 | 4 | 22.2% | 30.8% |
| 33110 | 26 | 6 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 23.1% | 60.0% |
| 33201 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 28.6% | 66.7% |
| 33202 | 19 | 4 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 21.1% | 33.3% |
| 33203 | 22 | 5 | 13 | 0 | 5 | 22.7% | 38.5% |
| 33210 | 40 | 8 | 29 | 0 | 8 | 20.0% | 27.6% |
| 33920 | 60 | 12 | 27 | 0 | 12 | 20.0% | 44.4% |
| 38100 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 25.0% | 33.3% |
| West | |||||||
| 40101 | 14 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 21.4% | 30.0% |
| 40102 | 81 | 17 | 73 | 0 | 17 | 21.0% | 23.3% |
| 40103 | 52 | 11 | 46 | 0 | 11 | 21.2% | 23.9% |
| 40110 | 91 | 19 | 77 | 0 | 19 | 20.9% | 24.7% |
| 40201 | 24 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 20.8% | 33.3% |
| 40202 | 56 | 12 | 47 | 0 | 12 | 21.4% | 25.5% |
| 40203 | 28 | 6 | 16 | 0 | 6 | 21.4% | 37.5% |
| 40210 | 42 | 9 | 26 | 0 | 9 | 21.4% | 34.6% |
| 40321 | 35 | 7 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 20.0% | 50.0% |
| 40324 | 61 | 13 | 33 | 0 | 13 | 21.3% | 39.4% |
| 40421 | 92 | 19 | 38 | 0 | 19 | 20.7% | 50.0% |
| 40424 | 76 | 16 | 45 | 0 | 16 | 21.1% | 35.6% |
| 41810 | 38 | 8 | 29 | 0 | 8 | 21.1% | 27.6% |
| 42103 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 50.0% | 50.0% |
| 42110 | 28 | 6 | 21 | 0 | 6 | 21.4% | 28.6% |
| 42204 | 13 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 23.1% | 37.5% |
| 42210 | 30 | 6 | 17 | 0 | 6 | 20.0% | 35.3% |
| 43102 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 20.0% | 40.0% |
| 43103 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 50.0% | 66.7% |
| 43110 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 22.2% | 66.7% |
| 43200 | 29 | 6 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 20.7% | 54.5% |
| 43210 | 17 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 17.6% | 100.0% |
| 43920 | 41 | 9 | 19 | 0 | 9 | 22.0% | 47.4% |
| 48102 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 20.0% | 28.6% |
Source: HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample, 2016
Table A.7. Different Types of ED Events in the NEDS, 2016
| ED Event | Number of ED Visits | Percent of ED Visits |
|---|---|---|
| ED visit in which the patient is treated and released | 123,089,247 | 85.0 |
| ED visit in which the patient is admitted to this same hospital | 18,955,851 | 13.1 |
| ED visit in which the patient is transferred to another short-term hospital | 2,363,592 | 1.6 |
| ED visit in which the patient died in the ED | 197,938 | 0.1 |
| ED visit in which patient is not admitted to the same hospital, destination unknown | 235,368 | 0.2 |
| ED visit in which the patient is discharged alive, destination unknown (but not admitted) | 746 | 0.0 |
Source: HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample, 2016.
Appendix B: Partner-Specific Restrictions
The table below enumerates the types of restrictions applied to the 2016 Nationwide Emergency Department Sample. Restrictions include the following types:
Table B.1. Partner-Specific Restrictions
| Confidentiality of Hospitals |
|---|
Limitations on sampling to ensure hospital confidentiality:
|
| Confidentiality of Records |
Limitations on selected data elements to ensure patient confidentiality:
|
| Limited Reporting of Diagnosis Codes for Medical Misadventures and Adverse Effects |
|
| Missing Information for Specific Populations of Patients |
|
| Type of Data Element | HCUP Data Element | Coding Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Admission timing | AWEEKEND | Admission on weekend: (0) admission on Monday-Friday, (1) admission on Saturday-Sunday |
| AMONTH | Admission month coded from (1) January to (12) December | |
| Age at admission | AGE | Age in years coded 0-90 years. Any ages greater than 90 were set to 90. | Diagnosis information | I10_DX1 - I10_DX30 | ICD-10-CM diagnoses |
| I10_NDX | Number of diagnoses coded on the original record received from Partner organizations | |
| I10_ECAUSE1 - I10_ECAUSE4 | ICD-10-CM external cause of morbidity codes | |
| I10_NECAUSE | Number of external cause of morbidity codes coded on the original record received from Partner organizations | |
| DXVER | Diagnosis version | |
| Discharge timing | DQTR | Discharge quarter coded: (1) Jan - Mar, (2) Apr - Jun, (3) Jul - Sep, (4) Oct - Dec |
| YEAR | Calendar year of ED visits | |
| Disposition of patient from the ED | DISP_ED | Disposition from ED: (1) routine, (2) transfer to short-term hospital, (5) other transfers, including skilled nursing facility, intermediate care, and another type of facility, (6) home health care, (7) against medical advice, (9) admitted as an inpatient to this hospital, (20) died in ED, (21) Discharged/transferred to court/law enforcement , (98) not admitted, destination unknown, (99) discharged alive, destination unknown (but not admitted) |
| DIED_VISIT | Died in ED: (0) did not die (1) died in the ED, (2) died in the hospital | |
| ED event | EDevent | Type of ED visit: (1) ED visit in which the patient is treated and released, (2) ED visit in which the patient is admitted to this same hospital, (3) ED visit in which the patient is transferred to another short-term hospital, (9) ED visit in which the patient died in the ED, (98) ED visits in which patient was not admitted, destination unknown, (99) ED visit in which patient was discharged alive, destination unknown (but not admitted) |
| Sex of patient | FEMALE | Indicates sex: (0) male, (1) female |
| Urban-rural location of the patient’s residence | PL_NCHS | Urban—rural designation for patient's county of residence: (1) large central metropolitan, (2) large fringe metropolitan, (3) medium metropolitan, (4) small metropolitan, (5) micropolitan, (6) not metropolitan or micropolitan |
| National quartile for median household income of patient's ZIP Code | ZIPINC_QRTL | Median household income quartiles for patient's ZIP Code. For 2016, the median income quartiles are defined as: 1) $1 - $42,999; (2) $43,000 - $53,999; (3) $54,000 - $70,999; and (4) $71,000 or more. |
| Payer information | PAY1 | Expected primary payer, uniform: (1) Medicare, (2) Medicaid, (3) private including HMO, (4) self-pay, (5) no charge, (6) other |
| PAY2 | Expected secondary payer, uniform: (1) Medicare, (2) Medicaid, (3) private including HMO, (4) self-pay, (5) no charge, (6) other | |
| Total ED charges | TOTCHG_ED | Total charges for ED services, edited |
| HCUP source file | HCUPFILE | Source of HCUP record: (SEDD) from SEDD file, (SID) from SID file |
| Discharge weight | DISCWT | Discharge weight used to calculate national estimates. Weights ED visits to AHA universe. |
| NEDS Hospital identifier, synthetic | HOSP_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS hospital number — links to NEDS Hospital weights file, but not to other HCUP databases |
| NEDS Stratum | NEDS_STRATUM | Stratum used to sample hospitals, based on geographic region, trauma, location/teaching status, and control. Stratum information is also contained in the Hospital Weights file. |
| Record identifier, synthetic | KEY_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS record number - links to NEDS Supplemental files, but not to other HCUP databases |
Table C.2. Data Elements in the 2016 NEDS Supplemental ED File
For prior years, refer to the NEDS Description of Data Elements page on the HCUP-US website or to previous versions of the NEDS Introduction.
| Type of Data Element | HCUP Data Element | Coding Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CPT procedure information | CPT1 — CPT15 | CPT procedures performed in the ED |
| CPTCCS1 — CPTCCS15 | Clinical Classifications Software (CCS) category for all CPT procedures | |
| NCPT | Number of procedures coded on the original record. A maximum of 15 CPT codes are retained on the NEDS. | |
| NEDS Hospital identifier, synthetic | HOSP_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS hospital number — links to NEDS Hospital Weights file, but not to other HCUP databases |
| Record identifier, synthetic | KEY_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS record number — links to NEDS Supplemental files, but not to other HCUP databases |
Data elements derived from AHRQ software tools (e.g., Clinical Classification Software (CCS) and the Elixhauser Comorbidity Software) are not available in the 2016 NEDS because the ICD10-CM/PCS versions are still under development. For users interested in applying the AHRQ software tools to the ICD-10-CM/PCS data in the 2016 NEDS, beta versions of the AHRQ software tools are available for download on the HCUP Tools & Software section of the HCUP-US website. A tutorial is available to users interested in applying the AHRQ software tools to the 2016 NEDS at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/tech_assist/tutorials.jsp.
For data years prior to 2016, refer to the NEDS Description of Data Elements page on the HCUP-US website or to previous versions of the NEDS Introduction.
Table C.3.Data Elements in the 2016 NEDS Supplemental Inpatient File
For prior years, refer to the NEDS Description of Data Elements page on the HCUP-US website or to previous versions of the NEDS Introduction.
| Type of Data Element | HCUP Data Element | Coding Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Disposition of patient from the hospital | DISP_IP | Disposition from hospital admission: (1) routine, (2) transfer to short-term hospital, (5) other transfers, including skilled nursing facility, intermediate care, and another type of facility, (6) home health care, (7) against medical advice, (20) died in hospital, (99) discharged alive, destination unknown |
| Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) | DRG | DRG in use on discharge date |
| DRG_NoPOA | DRG assignment made without the use of the present on admission flags for the diagnoses | |
| DRGVER | Grouper version in use on discharge date | |
| MDC | Major Diagnosis Category (MDC) in use on discharge date | |
| MDC_NoPOA | MDC in use on discharge date, calculated without the use of the present on admission flags for the diagnoses | |
| Length of hospital inpatient stay | LOS_IP | Length of stay, edited |
| Total charges for inpatient stay | TOTCHG_IP | Total charges for ED and inpatient services, edited |
| ICD-10-PCS procedure information | I10_PR_IP1 - I10_PRI_IP9 | ICD-10-PCS procedures coded on ED admissions. Procedure may have been performed in the ED or during the hospital stay. |
| I10_NPR_IP | Number of procedures coded on the original record. | |
| PRVER | Procedure version | |
| NEDS Hospital identifier, synthetic | HOSP_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS hospital number - links to NEDS Hospital Weights file, but not to other HCUP databases |
| Record identifier, synthetic | KEY_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS record number - links to NEDS Supplemental files, but not to other HCUP databases |
Table C.4. Data Elements in the 2016 NEDS Hospital Weights File
For prior years, refer to the refer to the NEDS Description of Data Elements page on the HCUP-US website or to previous versions of the NEDS Introduction.
| Type of Data Element | HCUP Data Element | Coding Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge counts | N_DISC_U | Number of AHA universe ED visits in the stratum |
| S_DISC_U | Number of sampled ED visits in the sampling stratum | |
| TOTAL_EDvisits | Total number of ED visits for this hospital in the NEDS | |
| Weights | DISCWT | Discharge weight used to calculate national estimates. Weights ED visits to AHA universe. |
| HOSPWT | Weight to hospital-owned EDs in AHA universe (i.e., total U.S.) | |
| Discharge Year | YEAR | Discharge year |
| Hospital counts | N_HOSP_U | Number of AHA universe hospital-owned EDs in the stratum |
| S_HOSP_U | Number of sampled hospital-owned EDs in the stratum | |
| NEDS Hospital identifier, synthetic | HOSP_ED | Unique HCUP NEDS hospital number — links to NEDS Hospital Weights file, but not to other HCUP databases |
| Hospital characteristics | HOSP_URCAT4 | Hospital urban-rural location: (1) large metropolitan areas with at least 1 million residents, (2) small metropolitan areas with less than 1 million residents, (3) micropolitan areas, (4) not metropolitan or micropolitan, (6) collapsed category of any urban-rural location, (7) collapsed category of small metropolitan and micropolitan, (8) metropolitan, collapsed category of large and small metropolitan, (9) non-metropolitan, collapsed category of micropolitan and rural |
| HOSP_CONTROL | Control/ownership of hospital: (0) government or private, collapsed category, (1) government, nonfederal, public, (2) private, non-profit, voluntary, (3) private, invest-own, (4) private, collapsed category | |
| HOSP_REGION | Region of hospital: (1) Northeast, (2) Midwest, (3) South, (4) West | |
| HOSP_TRAUMA | Trauma center level: (0) nontrauma center, (1) trauma level I, (2) trauma level II (3) trauma level III, (4) nontrauma or trauma level III, collapsed category beginning in the 2011 NEDS, (8) trauma level I or II, collapsed category (9) trauma level I, II, or III, collapsed category in the 2006-2010 NEDS. Children's hospitals with trauma centers are classified with adult/pediatric trauma centers. | |
| HOSP_UR_TEACH | Teaching status of hospital: (0) metropolitan non-teaching, (1) metropolitan teaching, (2) non-metropolitan | |
| NEDS_STRATUM | Stratum used to sample EDs, includes geographic region, trauma, location/teaching status, and control |
Appendix D: Comparisons of the NEDS with Existing Sources of ED Data
Figure D.1. Emergency Department Visit Counts in the United States, 2016
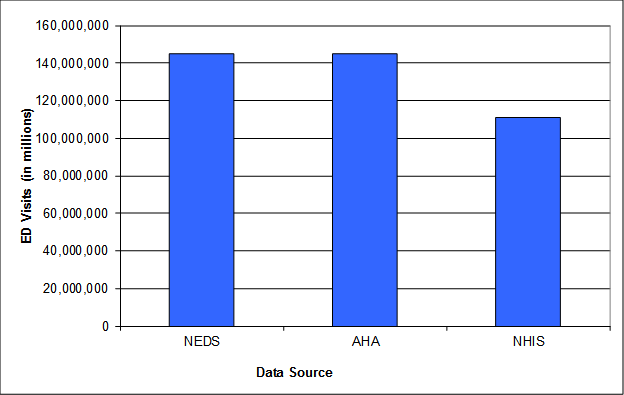
Notes: ED = emergency department; NEDS = HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample; AHA = American Hospital Association Annual Survey Database; NHIS = National Health Interview Survey.
The above graphic outlines the number of emergency department visits in the United States in 2016. For 2016 it is estimated to be 144,842,742 according to the HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS); 144,842,742 according to the American Hospital Association Annual Survey Database (AHA); and 110,990,623 according to the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS).
Table D.1. Estimates of ED Visits by U.S. Geographic Region from Four ED Data Sources, 2016
| ED Visits | ED Data Sources | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEDS1 | AHA | NHIS 2 | ||||||
| N (weighted) | %3 | N | %3 | N | %3 | |||
| By Census Region | ||||||||
| Northeast | 26,474,638 | 18.3 | 26,474,638 | 18.3 | 20,040,211 | 18.1 | ||
| Midwest | 32,939,409 | 22.7 | 32,939,409 | 22.7 | 27,485,397 | 24.8 | ||
| South | 58,096,752 | 40.1 | 58,096,752 | 40.1 | 41,147,176 | 37.1 | ||
| West | 27,331,943 | 18.9 | 27,331,943 | 18.9 | 22,317,840 | 20.1 | ||
| Total U.S. | 144,842,742 | 100.0 | 144,842,742 | 100.0 | 110,990,623 | 100.0 | ||
| Notes: ED = emergency department; NEDS = HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample; AHA = American Hospital Association Annual Survey Database; NHIS = National Health Interview Survey.
1 NEDS weighted counts by geographic region exactly match the AHA counts because the AHA data were used as control totals for the NEDS discharge weights. 2 NHIS estimates were calculated using the midpoint of the ranges provided in the survey (0, 1, 2-3, 4-5, 6-7, 8-9, 10-12, and 13-15). For the upper range of visits in the survey (16 or more ED visits), 16 ED visits were used for the estimate. 3 Column percent indicates the percentage of the total records in the ED data source that are in the Census region. |
||||||||
Table D.2. Estimates of the ED Visits Resulting in Inpatient Admissions (Admission Rate) by U.S. Geographic Region, 2016
| ED Visits Resulting in Inpatient Admissions | ED Data Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| NEDS | ||
| N (weighted) | % of all ED Visits | |
| By Census Region | ||
| Northeast | 3,918,069 | 14.8 |
| Midwest | 4,023,239 | 12.2 |
| South | 7,729,011 | 13.3 |
| West | 3,285,532 | 12.0 |
| Total U.S. | 18,955,851 | 13.1 |
Notes: ED = emergency department; NEDS = HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample
Table D.3. Estimates of the Number of Hospital-Owned EDs by ED Visit Volume from Three ED Data Sources, 2016
| Volume of ED Visits in 2016 | Data Sources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEDS | AHA | N (weighted) | %1 | N | %1 | |
| Less than 10,000 visits | 1,445 | 31.8 | 1,493 | 32.8 | ||
| 10,000 - 19,999 visits | 726 | 16.0 | 756 | 16.6 | ||
| 20,000 - 29,999 visits | 523 | 11.5 | 530 | 11.6 | ||
| 30,000 - 39,999 visits | 488 | 10.7 | 447 | 9.8 | ||
| 40,000 - 49,999 visits | 341 | 7.5 | 319 | 7.0 | ||
| 50,000 or more visits | 1,028 | 22.6 | 1007 | 22.1 | ||
| All Hospital-owned EDs | 4,552 | 100.00 | 4,552 | 100.00 | ||
Notes: ED = emergency department; NEDS = Nationwide Emergency Department Sample from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project; AHA = American Hospital Association Annual Survey Database.
1Column percent indicates the percentage of the total records in the ED data source that are in each group of ED visits.
Table D.4. Estimates of the Number of ED Visits Related to Nonfatal Injures from Two ED Data Sources, 2016 (Revised 9/30/19)
| ED Data Source | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEDS (All injuries)1 | NEDS (Initial Encounter for Injury) | NEISS-AIP2 | N (weighted) | 95% Confidence Interval | N (weighted) | 95% Confidence Interval | N (weighted) | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Total number of ED visits for nonfatal injuries | 30,277,615 | (28,823,559, 31,731,671) |
29,454,464 | (28,043,380, 30,865,548) |
32,074,270 | (27,070,733, 37,077,807) |
| By discharge status from the ED | ||||||
| Treated and released from the ED | 27,154,558 | (25,824,976, 28,484,140) |
26,474,410 | (25,181,945, 27,766,874) |
27,526,500 | (23,077,677, 31,975,323) |
| Admitted to the same hospital | 2,431,325 | (2,281,794, 2,580,856) |
2,302,103 | (2,158,976, 2,445,230) |
2,880,270 | (2,231,400, 35,291,41) |
| Transferred | 482,952 | (448,733, 517,170) |
475,209 | (441,821, 508,597) |
621,495 | (477,141, 765,848) |
| Other3 | 208,780 | (189,929, 227,632) |
202,743 | (184,480, 221,005) |
1,046,005 | (99,784, 1,992,226) |
Notes: ED = emergency department; NEDS = Nationwide Emergency Department Sample from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project; NEISS-AIP = National Electronic Injury Surveillance System All-Injury Program.
1 Any diagnosis in the following range: All codes starting with S, codes starting with T07-T34, codes starting with T36-T50 with a 6th character of 1, 2, 3, or 4 (Exceptions: T36.9, T37.9, T39.9, T41.4, T42.7, T43.9, T45.9, T47.9, and T49.9 with a 5th character of 1, 2, 3, or 4), codes starting with T51-T65, codes starting with T66-T76, codes starting with T79, codes T84.01 and T84.02, and codes O9A.2-O9A.5. Counts for all injuries allowed any 7th character for the injury diagnosis code; counts for the initial encounter limited injury diagnosis codes to those with a 7th character of A, B, C, or missing.
2 Data from WISQARS Query System (https://webappa.cdc.gov/sasweb/ncipc/nfirates.html). Includes non-fatal, all-cause injuries. Patients who died on arrival to the ED or during treatment in the ED are excluded. Queried September 20, 2018.
3 For the NEISS-AIP, other includes left against medical advice, sent for observations, and unknown destination. For the NEDS, other include left against medical advice. Patients who are treated in the ED and then observed cannot be identified. If they were discharged home from observation, they are counted under "treated and released from the ED"; if they were admitted to the hospital from observation, they are counted under "admitted to the same hospital".
1 Merrill, C. T. and Owens, P. L. (2007). Hospital Admissions That Began in the Emergency Department for Children and Adolescents, 2004. HCUP Statistical Brief #32. June 2007. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. Retrieved June 9, 2008 from www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb32.pdf
2 Merrill, C. T. and Owens, P. L. (2007). Hospital Admissions That Began in the Emergency Department for Children and Adolescents, 2004. HCUP Statistical Brief #32. June 2007. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. Retrieved June 9, 2008 from www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb32.pdf.
3 ICD-10-CM/PCS: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification/Procedure Coding System
4 More of the AHA "community hospital designation" is available at http://www.ahadataviewer.com/glossary. ![]()
5 MacKenzie EJ, Hoyt DB, Sacra JC, et al. National inventory of hospital trauma centers. JAMA. 2003;289:1515-1522
.
6 American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma, Verification, Review, and Consultation Program for Hospitals. Additional details are available at https://www.facs.org/quality-programs/trauma/vrc. ![]() Accessed September 2018.
Accessed September 2018.
7 American Trauma Society. Trauma Information Exchange Program. Available at: http://www.amtrauma.org/?page=TIEP. ![]() Accessed September 2018.
Accessed September 2018.
8 United States Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service (https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/urban-influence-codes.aspx)
9 The collapsing of small metropolitan and micropolitan areas was required in the South in 2011-2015.
10 The collapsing of all areas was required in the South in 2014.
11The ZIP Code of the hospital is not included in the NEDS data files.
12 This HCUP Methods Series report is available at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/methods/2011_03.pdf.
13 Carlson BL, Johnson AE, Cohen SB. An evaluation of the use of personal computers for variance estimation with complex survey data. J Off Statistics. 1993;9(4):795-814.
14 At the time this document was created, the 2016 NHAMCS public use file was not available for developing comparative estimates.
| Internet Citation: 2016 Introduction to the NEDS. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). February 2020. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/neds/NEDS_Introduction_2016.jsp. |
| Are you having problems viewing or printing pages on this website? |
| If you have comments, suggestions, and/or questions, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| If you are experiencing issues related to Section 508 accessibility of information on this website, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| Privacy Notice, Viewers & Players |
| Last modified 2/5/20 |