|
TABLE OF CONTENTS HIGHLIGHTS INTRODUCTION HCUP PARTNERS 1. OVERVIEW 2. DIAGNOSES 3. PROCEDURES 4. COSTS 5. WOMEN'S HEALTH SOURCES/METHODS DEFINITIONS FOR MORE INFO ACKNOWLEDGMENTS CITATION FACTS & FIGURES 2009 PDF |
EXHIBIT 1.3 Expected Primary Payer (PDF)
1.3a
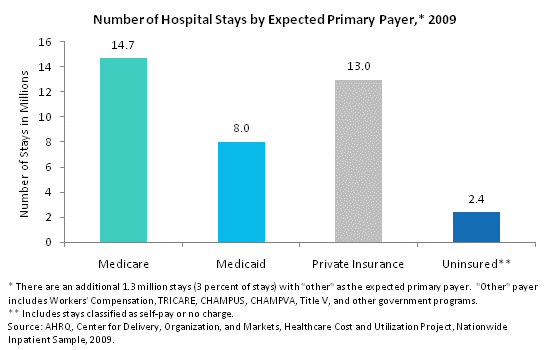
Number of hospital stays by expected primary payer, 2009. Column chart. Number of stays in millions. Medicare: 14.7; Medicaid: 8.0; private insurance: 13.0; uninsured: 2.4. Note: There are an additional 1.3 million stays (3% of stays) with "other" as the expected primary payer. "Other" payer includes Workers' Compensation, TRICARE, CHAMPUS, CHAMPVA, Title V, and other government programs. Note: Uninsured includes stays classified as self-pay or no charge. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 2009.
The primary payer bears the major financial responsibility for the hospital stay. Although other payers, including the patients themselves, may also pay part of the cost of hospitalization, only the expected primary payers are depicted in this section.
1.3b
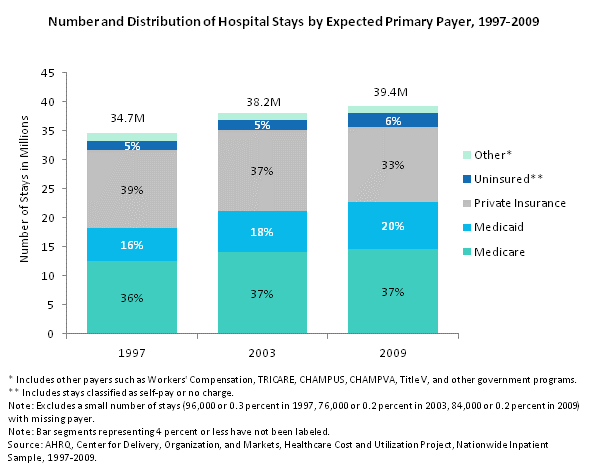
Number and distribution of hospital stays by expected primary payer, 1997 through 2009. Column chart. Number of stays in millions. 1997: 34.7; 2003: 38.2; 2009: 39.4. Distribution of stays. 1997: other: 4%; uninsured: 5%; private insurance: 39%; Medicaid: 16%; Medicare: 36%. 2003: other: 3%; uninsured: 5%; private insurance: 37%; Medicaid: 18%; Medicare: 37%. 2009: other: 3%; uninsured: 6%; private insurance: 33%; Medicaid: 20%; Medicare: 37%. Note: Other includes payers such as Workers' Compensation, TRICARE, CHAMPUS, CHAMPVA, Title V, and other government programs. Note: Uninsured includes stays classified as self-pay or no charge. Note: Excludes a small number of stays (96,000 or 0.3 percent in 1997, 76,000 or 0.2 percent in 2003, 84,000 or 0.2 percent in 2009) with missing payer. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
The number of stays increased steadily in the 12-year period, growing from 34.7 million in 1997 to 39.4 million in 2009.
1.3c
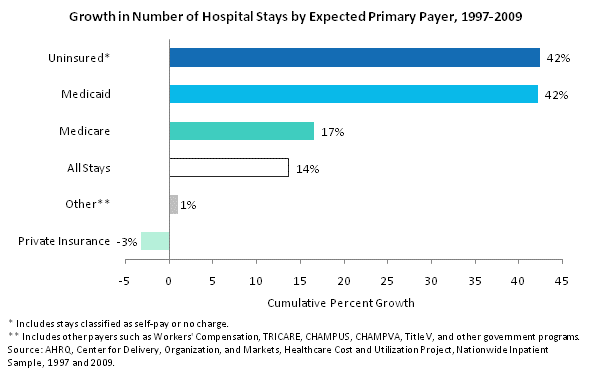
Growth in number of hospital stays by expected primary payer, 1997 through 2009. Bar chart. Cumulative percent growth.
Uninsured: 42%; Medicaid: 42%; Medicare: 17%; all stays: 14%; other: 1%; private insurance: -3%. Note: Uninsured includes stays classified as self-pay or no charge. Note: Other includes payers such as Workers' Compensation, TRICARE, CHAMPUS, CHAMPVA, Title V, and other government programs. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997 and 2009.
Between 1997 and 2009, the number of hospital stays grew by 14 percent; however, growth varied widely by expected primary payer.
1 National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2010: With Special Feature on Death and Dying. Hyattsville, MD, 2011.
|
| Internet Citation: Facts and Figures 2009 Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). November 2011. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/factsandfigures/2009/exhibit1_3.jsp. |
| Are you having problems viewing or printing pages on this website? |
| If you have comments, suggestions, and/or questions, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| If you are experiencing issues related to Section 508 accessibility of information on this website, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| Privacy Notice, Viewers & Players |
| Last modified 11/9/11 |