|
TABLE OF CONTENTS HIGHLIGHTS INTRODUCTION HCUP PARTNERS 1. OVERVIEW 2. DIAGNOSES 3. PROCEDURES 4. COSTS 5. WOMEN'S HEALTH SOURCES/METHODS DEFINITIONS FOR MORE INFO ACKNOWLEDGMENTS CITATION FACTS & FIGURES 2009 PDF |
EXHIBIT 5.6 Childbirth (PDF) 5.6a
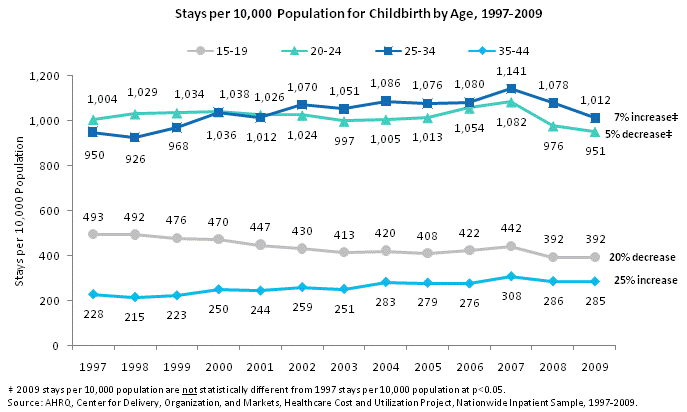
Stays per 10,000 population for childbirth by age, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Stays per 10,000 population. 15 to 19. 20% decrease between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 493; 1998: 492; 1999: 476; 2000: 470; 2001: 447; 2002: 430; 2003: 413; 2004: 420; 2005: 408; 2006: 422; 2007: 442; 2008: 392; 2009: 392. 20-24. 5% decrease not statistically significant. 1997: 1,004; 1998: 1,029; 1999: 1,034; 2000: 1,038; 2001: 1,026; 2002: 1,024; 2003: 997; 2004: 1,005; 2005: 1,013; 2006: 1,054; 2007: 1,082; 2008: 976; 2009: 951. 25-34. 7% increase not statistically significant. 1997: 950; 1998: 926; 1999: 968; 2000: 1,036; 2001: 1,012; 2002: 1,070; 2003: 1,051; 2004: 1,086; 2005: 1,076; 2006: 1,080; 2007: 1,141; 2008: 1,078; 2009: 1,012. 35-44. 25% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 228; 1998: 215; 1999: 223; 2000: 250; 2001: 244; 2002: 259; 2003: 251; 2004: 283; 2005: 279; 2006: 276; 2007: 308; 2008: 286; 2009: 285. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
5.6b
5.6c
5.6d
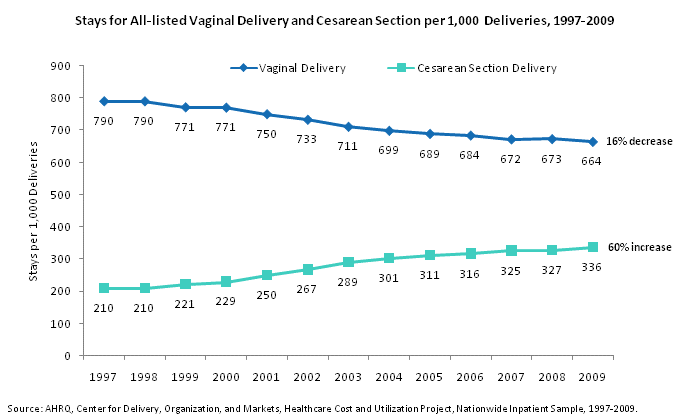
Stays for all-listed vaginal delivery and Cesarean section per 1,000 deliveries, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Stays per 1,000 deliveries. Vaginal delivery. 16% decrease between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 790; 1998: 790; 1999: 771; 2000: 771; 2001: 750; 2002: 733; 2003: 711; 2004: 699; 2005: 689; 2006: 684; 2007: 672; 2008: 673; 2009: 664. Cesarean section delivery. 60% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 210; 1998: 210; 1999: 221; 2000: 229; 2001: 250; 2002: 267; 2003: 289; 2004: 301; 2005: 311; 2006: 316; 2007: 325; 2008: 327; 2009: 336. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
5.6e 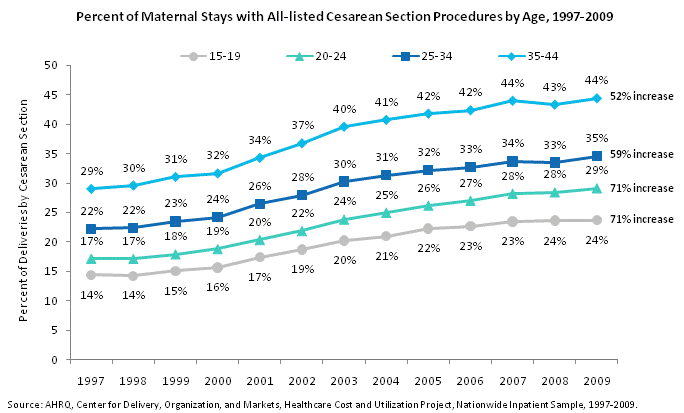
Percent of maternal stays with all-listed Cesarean section procedures by age, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Percent of deliveries by Cesarean section. 15 to 19. 71% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 14%; 1998: 14%; 1999: 15%; 2000: 16%; 2001: 17%; 2002: 19%; 2003: 20%; 2004: 21%; 2005: 22%; 2006: 23%; 2007: 23%; 2008: 24%; 2009: 24%. 20-24. 71% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 17%; 1998: 17%; 1999: 18%; 2000: 19%; 2001: 20%; 2002: 22%; 2003: 24%; 2004: 25%; 2005: 26%; 2006: 27%; 2007: 28%; 2008: 28%; 2009: 29%. 25-34. 59% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 22%; 1998: 22%; 1999: 23%; 2000: 24%; 2001: 26%; 2002: 28%; 2003: 30%; 2004: 31%; 2005: 32%; 2006: 33%; 2007: 34%; 2008: 33%; 2009: 35%. 35-44. 52% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 29%; 1998: 30%; 1999: 31%; 2000: 32%; 2001: 34%; 2002: 37%; 2003: 40%; 2004: 41%; 2005: 42%; 2006: 42%; 2007: 44%; 2008: 43%; 2009: 44%. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
5.6f
Stays for all-listed vaginal deliveries with and without episiotomy and perineal lacerations per 1,000 deliveries, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Stays per 1,000 deliveries. Vaginal delivery without episiotomy. 4% increase between 1997 and 2009 not statistically significant. 1997: 564; 1998: 583; 1999: 578; 2000: 589; 2001: 582; 2002: 584; 2003: 572; 2004: 576; 2005: 584; 2006: 592; 2007: 588; 2008: 591; 2009: 588. Perineal lacerations. 9% increase between 1997 and 2009 not statistically significant. 1997: 303; 1998: 309; 1999: 308; 2000: 324; 2001: 316; 2002: 320; 2003: 309; 2004: 317; 2005: 318; 2006: 324; 2007: 320; 2008: 330; 2009: 329. Vaginal delivery with episiotomy. 66% decrease between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 227; 1998: 207; 1999: 201; 2000: 182; 2001: 168; 2002: 149; 2003: 139; 2004: 122; 2005: 105; 2006: 92; 2007: 84; 2008: 82; 2009: 77. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
5.6g
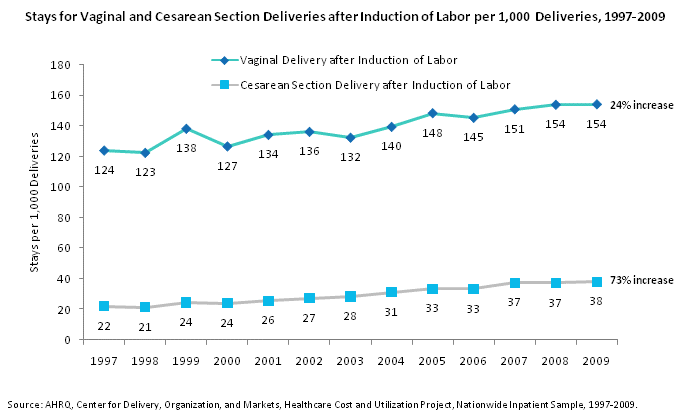
Stays for vaginal and Cesarean section deliveries after induction of labor per 1,000 deliveries, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Stays per 1,000 deliveries. Vaginal delivery after induction of labor. 24% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 124; 1998: 123; 1999: 138; 2000: 127; 2001: 134; 2002: 136; 2003: 132; 2004: 140; 2005: 148; 2006: 145; 2007: 151; 2008: 154; 2009: 154. Cesarean section delivery after induction of labor. 73% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 22; 1998: 21; 1999: 24; 2000: 24; 2001: 26; 2002: 27; 2003: 28; 2004: 31; 2005: 33; 2006: 33; 2007: 37; 2008: 37; 2009: 38. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
5.6h

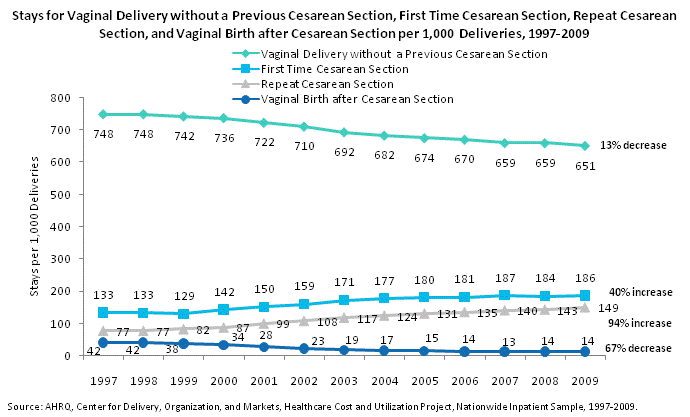
Stays for vaginal delivery without a previous Cesarean section, first time Cesarean section, repeat Cesarean section, and vaginal birth after Cesarean section per 1,000 deliveries, 1997 through 2009. Line chart. Stays per 1,000 deliveries. Vaginal delivery without a previous Cesarean section. 13% decrease between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 748; 1998: 748; 1999: 742; 2000: 736; 2001: 722; 2002: 710; 2003: 692; 2004: 682; 2005: 674; 2006: 670; 2007: 659; 2008: 659; 2009: 651. First time Cesarean section. 40% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 133; 1998: 133; 1999: 129; 2000: 142; 2001: 150; 2002: 159; 2003: 171; 2004: 177; 2005: 180; 2006: 181; 2007: 187; 2008: 184; 2009: 186. Repeat Cesarean section. 94% increase between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 77; 1998: 77; 1999: 82; 2000: 87; 2001: 99; 2002: 108; 2003: 117; 2004: 124; 2005: 131; 2006: 135; 2007: 140; 2008: 143; 2009: 149. Vaginal birth after Cesarean section. 67% decrease between 1997 and 2009. 1997: 42; 1998: 42; 1999: 38; 2000: 34; 2001: 28; 2002: 23; 2003: 19; 2004: 17; 2005: 15; 2006: 14; 2007: 13; 2008: 14; 2009: 14. Source: AHRQ, Center for Delivery, Organization, and Markets, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 1997-2009.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internet Citation: Facts and Figures 2009. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). February 2012. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/factsandfigures/2009/exhibit5_6.jsp. |
| Are you having problems viewing or printing pages on this website? |
| If you have comments, suggestions, and/or questions, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| If you are experiencing issues related to Section 508 accessibility of information on this website, please contact hcup@ahrq.gov. |
| Privacy Notice, Viewers & Players |
| Last modified 2/8/12 |